Azure Functions & Durable Functions 环境搭建 快速开始
前置条件
VSCode 安装
Azure Function 的 VSCode 插件安装
Azure Function Core Tools 下载
NodeJS 18 以上
安装微软的包密钥
1 2 curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | gpg --dearmor > microsoft.gpgmv microsoft.gpg /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/microsoft.gpg
设置源
1 sudo sh -c 'echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/debian/$(lsb_release -rs | cut -d' .' -f 1)/prod $(lsb_release -cs) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/dotnetdev.list'
需要做一些小小的修改
将 20 改为 10,因为我是 debian10 系列的主机
apricot 改为 buster
更新源
安装
1 sudo apt-get install azure-functions-core-tools-4
创建本地项目
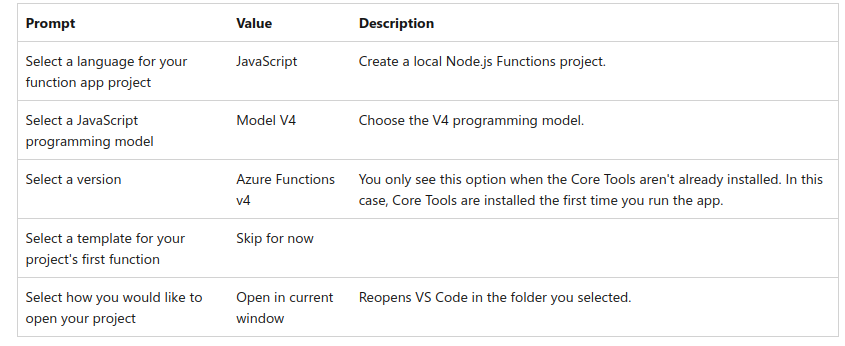
使用 VSCode 插件创建 New Project
选择一个空文件夹
完成以下设置
创建结果
安装 Durable Functions 包 1 npm install durable-functions@preview
创建函数 最基本的 Durable Functions 应用有三类基本的函数
Orchestrator function:描述一个编排其他 functions 的 workflowActivity function:由 orchestrator function 调用,执行工作,可能返回结果Client function:一个常规的 Azure Function 用来启动一个 orchestrator function
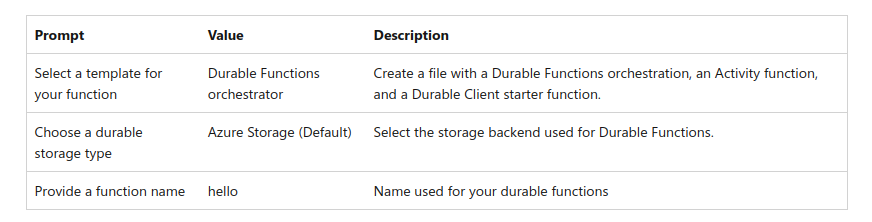
用 VSCode 创建一个 function
完成以下设置
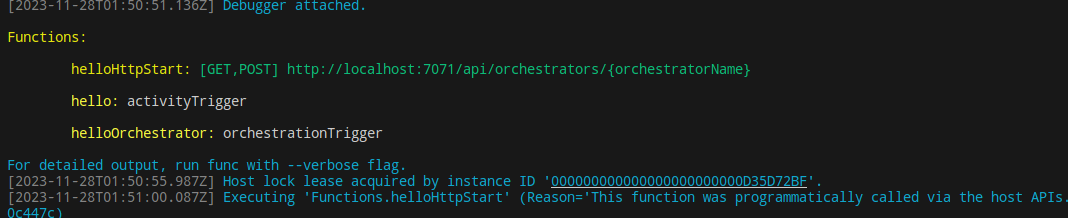
可以在 src/functions/hello.js 中看到函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 const { app } = require('@azure/functions' );df = require('durable-functions' );'hello' ;'helloOrchestrator' , function * (context) {'Tokyo' ));'Seattle' ));'Cairo' ));return outputs;return `Hello, ${input} `;'helloHttpStart' , {'orchestrators/{orchestratorName}' ,'${instanceId}' .`);return client.createCheckStatusResponse(request, instanceId);
在这个例子中
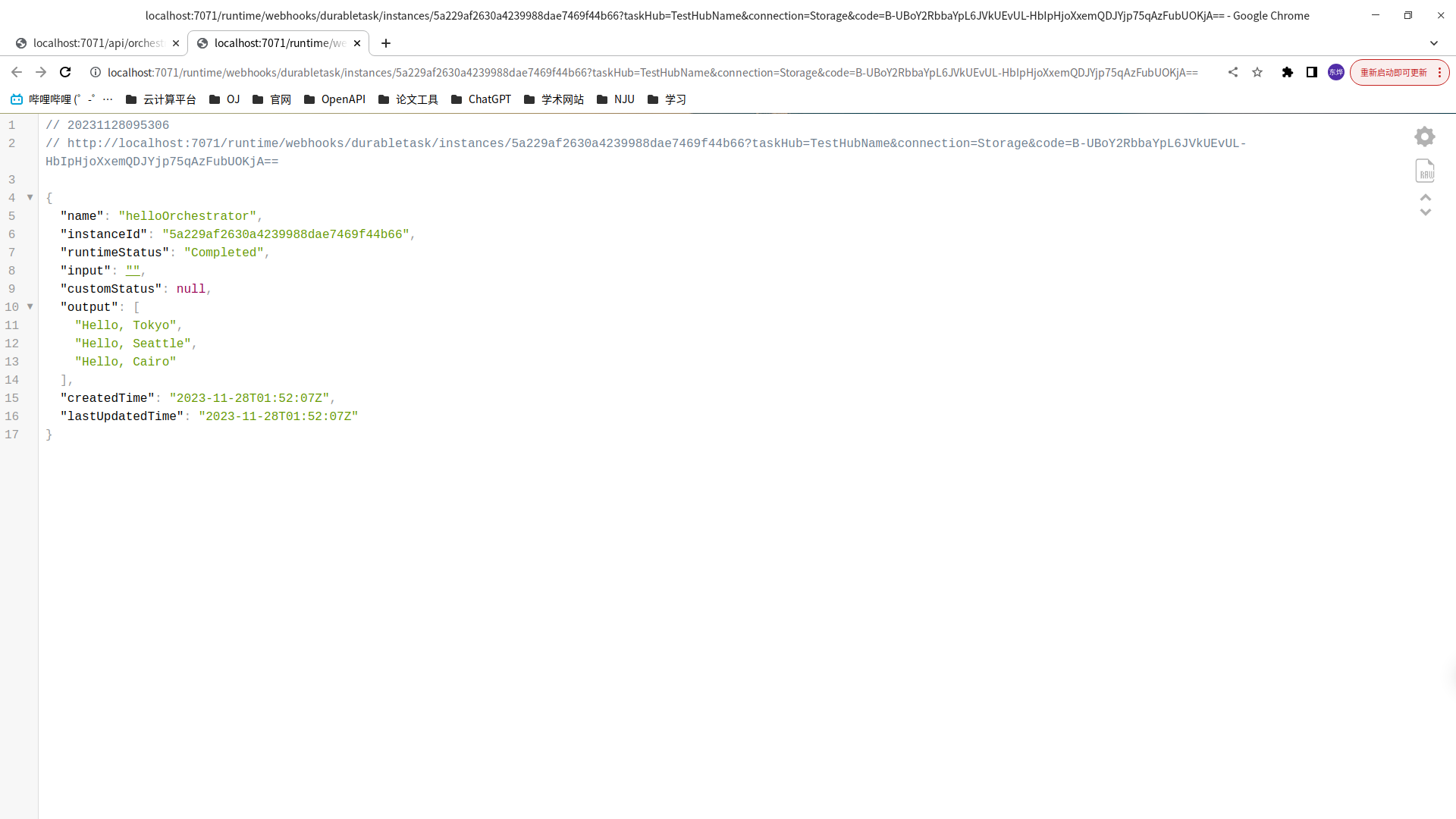
创建了一个名字为 helloOrchestrator 的编排函数
创建了一个叫做 hello 的活动函数
编排函数编排了多个活动函数
添加了一个 HTTP trigger 函数来启动编排函数
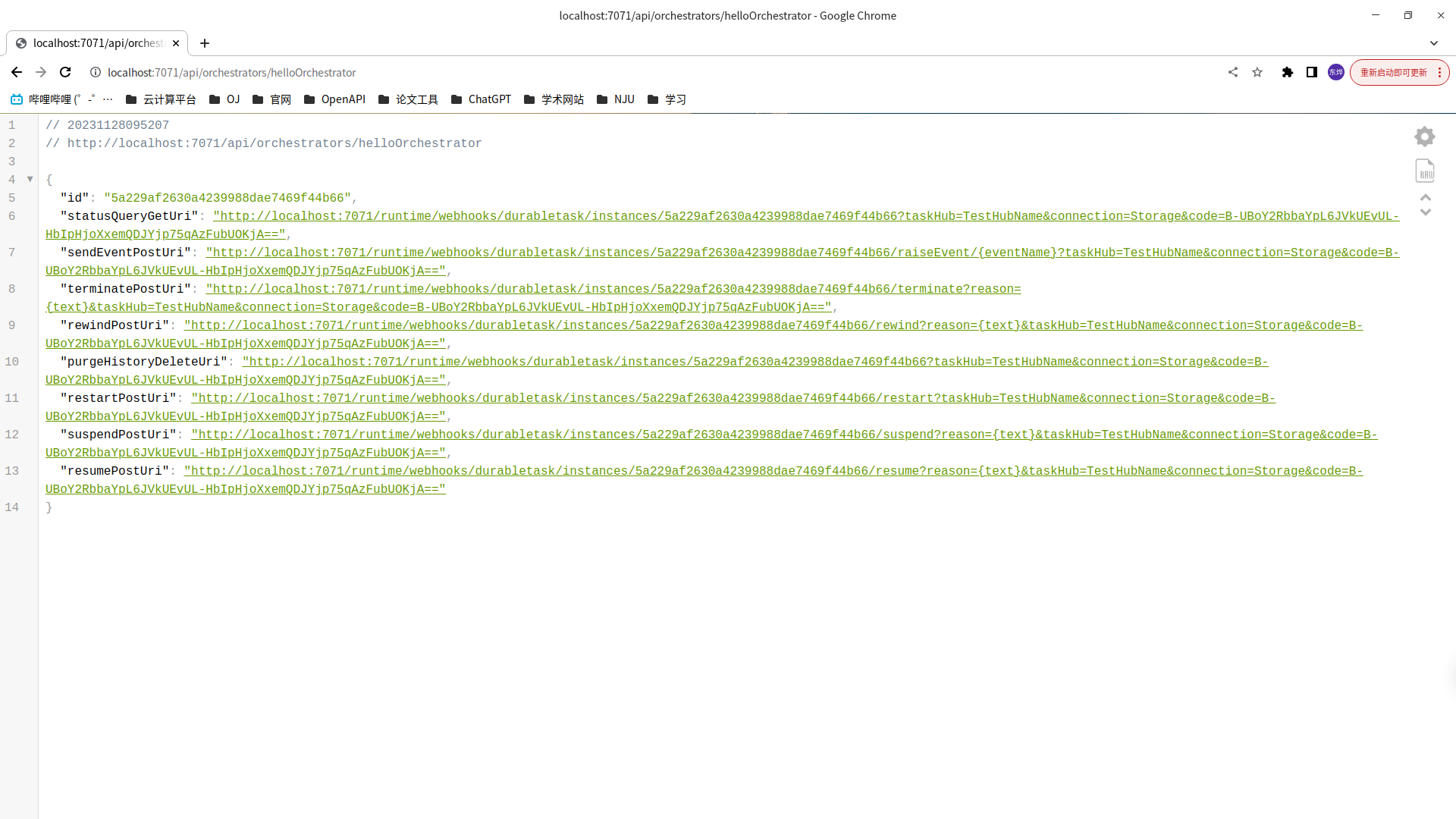
测试函数 本地模拟器
安装 Azurite 插件
启动所有 Azurite 服务
F5 运行
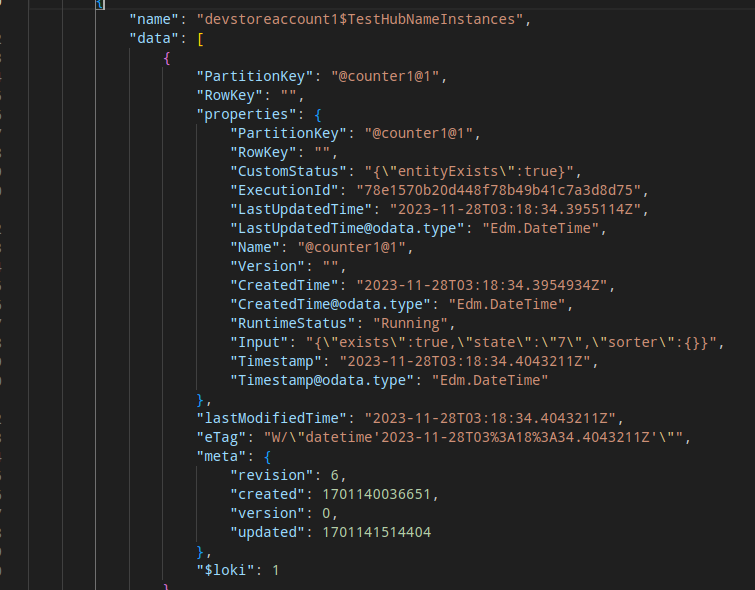
存储状态文件
相关概念 实体函数 实体的行为有点类似于通过消息进行通信的微型服务。 每个实体具有唯一的标识和内部状态(如果存在)。 与服务或对象一样,实体会根据提示执行操作。 执行的操作可能会更新实体的内部状态。 它还可能会调用外部服务并等待响应。 实体使用通过可靠队列隐式发送的消息来与其他实体、业务流程和客户端通信。
其内部存储的有关某个实体示例的信息如下图所示,其中的 input 字段
实现原理 可靠执行 DF 能够确保编排的可靠执行,这是通过使用存储队列来驱动函数的触发以及通过存放执行历史记录来实现的。
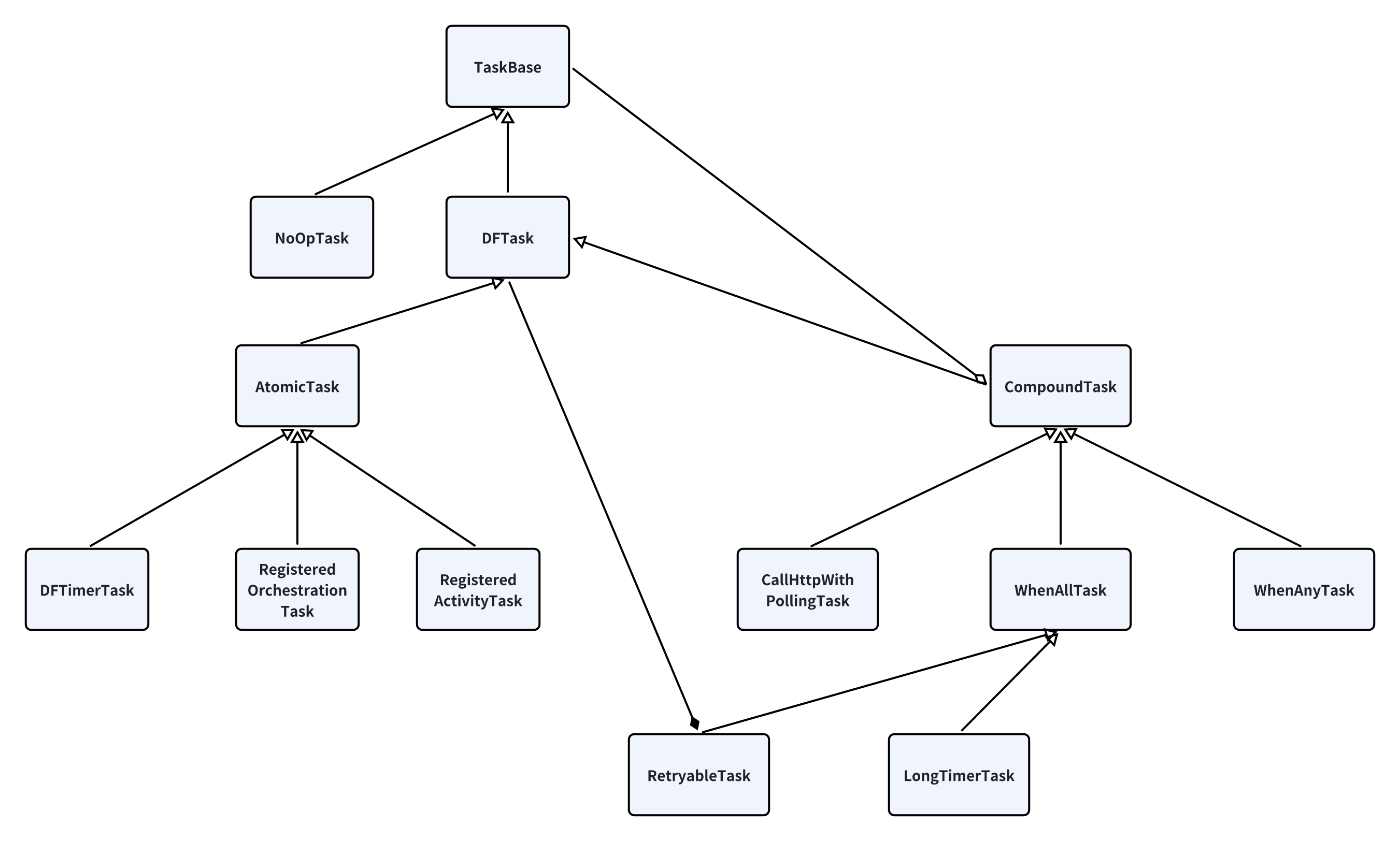
任务关键类
TaskBase所有任务的基类,定义了所有任务的基本状态转移
在 orchestrator 调用 callActicity 函数的时候,其内部会创建 AtomicTask 类,该类是 TaskBase 的一个子类
该类的内部存储了 task 的状态 state,表明该任务是 Running、Failed 或者 Completed
当任务(通常是 CompoundTask)调用这个函数时,会判断这个函数是否已经被执行过
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 propagate (executor?: TaskOrchestrationExecutor ): void {const hasCompleted = this .state !== TaskState .Running ;if (hasCompleted && this .parent !== undefined ) {this .parent .handleCompletion (this , executor);
DFTask该类简单继承了一下 TaskBase,增加了函数的回调操作
CompoundTask该类继承 DFTask,包含了多个 TaskBase,也就是维护了多个子任务
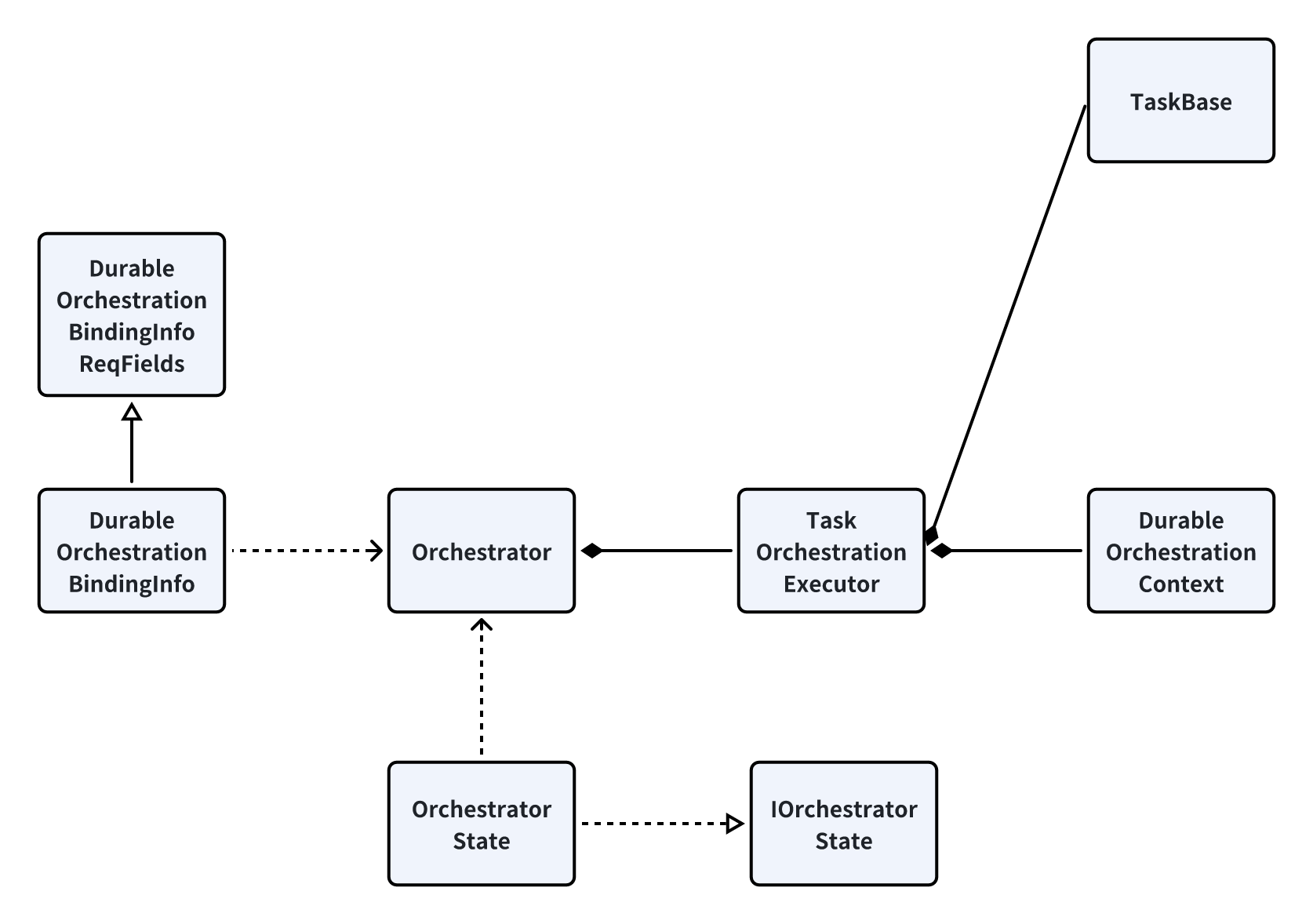
编排关键类
Orchestrator
负责监听一个编排触发器 DurableOrchestrationBindingInfo 以及处理维护一个上下文 OrchestrationContext,将结果返回给 OrchestratorState
处理的最后将上下文等信息交托给 TaskOrchestrationExecutor 继续执行
TaskOrchestrationExecutorexecute 函数负责管理一个编排函数的执行,并且通过历史记录进行重播
通过历史记录执行编排函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 for (const historyEvent of history) {this .processEvent (historyEvent);if (this .isDoneExecuting ()) {break ;
processEvent 函数的主要功能
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 private processEvent (event : HistoryEvent ): void {const eventType = event.EventType ;switch (eventType) {case HistoryEventType .OrchestratorStarted : {case HistoryEventType .ContinueAsNew : {case HistoryEventType .ExecutionStarted : {case HistoryEventType .EventSent : {default :
tryResumingUserCode 函数
如果当前执行的任务还在 running 则不能直接执行
如果整个编排函数执行完成了,则获取其返回值
如果结果生成器返回了一个 DFTask,那么就表示接下来要执行新的函数
然后编排函数再以递归的方式执行该函数
构建当前的编排状态
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 const actions : IAction [][] = this .actions .length == 0 ? [[]] : [this .actions ];const orchestratorState = new OrchestratorState ({isDone : this .hasCompletedSuccessfully (),actions : actions,output : this .output ,error : this .exception ?.message ,customStatus : this .context .customStatus ,schemaVersion : this .schemaVersion ,
DurableOrchestrationContext维护函数流的上下文