ElasticQuota
概述
Koordinator 简单介绍
QoS(Quality of Service,服务质量)是网络和系统中用于资源分配优先级和性能保障的技术机制,旨在确保关键服务在资源受限时仍能满足特定要求(如延迟、带宽、可靠性)
在Koordinator中,QoS用于表达Pod在该节点上的运行质量,比如获取资源的方式、获取资源的比例、QoS保障策略等
Koordinator 是一个为微服务基于Qos的编排工具,用于编排基于k8s部署的AI,大数据等应用。
他的诞生旨在在原有的k8s调度能力上做一定的增强,主要包括一下几个方面.
- 在集群中协调不同类型的工作负载以及在单点上能跑不同类型的
pods - 允许资源过度申请来提高资源的利用率,但是仍然能满足
QoS的保证 - 资源编排与资源隔离来提高各种批处理任务的效率
与k8s类似,Koordinator主要包括以下几个组件
Koord-Scheduler: 基于QoS敏感的任务调度器,用于任务管理。Koord-Descheduler: 负载感知调度,一个支持节点负载重新平衡的调度插件,支持用户定义节点的CPU负载级别,以避免热点节点Koord-Manager: 由多个控制器和 webhook 组成,用于协调共置工作负载并支持资源超额承诺调度和 SLO 管理。Koordlet: 作为DaemonSet部署在kubernetes集群中,用于支持colocation资源过量使用、干扰检测、QoS保证等。
K8S 本身的调度能力
K8S 下发任务的过程
- 用户提交
Pods定义
用户会通过kubectl将请求提交到了kube-apiserver组件中。
- Kube-ApiServer 层
- 认证:判断请求客户端的证书等信息(密钥管理),通过用户得到角色
- 鉴权:检查用户是否有权限创建
pods - 准入控制:
- ResourceQuota是否满足
- DefaultStorageClass
- PodSecurity安全策略
- 写入etcd
API-Server会将pods的元数据信息写入到etcd中
- 调度器(Kube-Scheduler)
- 监控未调度的
pods - 过滤:排除一些一定不能调度的节点(例如资源不足、亲和性不满足等)
- 打分:根据亲和性规则
- 绑定:将
pods与nodes节点进行绑定
kubelet接管
- 拉取镜像
- 创建沙箱
- 启动容器
K8S 下的 Resource Quota
Kubernetes的Resource Quota(资源配额)是一种集群管理机制,用于限制命名空间(Namespace)级别的资源使用总量,防止单个命名空间过度消耗 CPU、内存、存储等资源,从而保障集群的公平性和稳定性.
- 面向场景:不同的团队在不同的
namespaces下工作,ResourceQuota实现在namespace下的资源隔离 - 禁止超额:如果用户创建的资源超过了
ResourceQuota的限制,那么k8s会直接返回403 Forbidden禁止用户创建pods
但是k8s的Resource Quota是在kube-apiserver层面完成的,不具备资源借用的这种灵活性。
Koordinator scheduler
Koordinator Scheduler 是用于实现其资源高效利用率的一个调度器,相当于是kube-scheduler的一个升级版。Koord-Scheduler包含了许多用于任务调度的组件,例如elasticquota, Gang scheduling
容量调度
容量调度是 koord-scheduler 在共享集群中管理不同用户资源使用情况的一种能力。主要通过管理 ElasticQuota 来实现
绑定调度
Koordinator 的任务调度
- 资源隔离:在同一个节点上,一个或者一组
pods需要进行资源隔离,以防止对其他类型的pods的抢占,相当于划分成为了一个个静态的箱子。
通常我们会通过资源配额(Quota)进行资源隔离 - 资源抢占
- 在同一个配额下的抢占:高优先级的
pods会对低优先级的pods进行抢占 - 不同配额下的抢占:
koordinator scheduler通过ElasticQuota实现跨资源配额下的抢占
- 在同一个配额下的抢占:高优先级的
ElasticQuota
正如前文我们所介绍的,ElasticQuota是Koord-Scheduler一个重要的组件,其可以实现
- 不同quota组的借用与归还,忙的quota可以跟空闲的quota借用资源,当空闲quota变忙的时候可以还回去
- 它考虑了不同配额组之间的资源公平性,当繁忙配额组向空闲配额组借用资源时,可以按照一定的公平规则将资源分配给繁忙配额组。
Label 级别的隔离
- 我们可以通过以下方式创建一个
ElasticQuota
1 | |
- 并且创建一个
pods
1 | |
可以通过
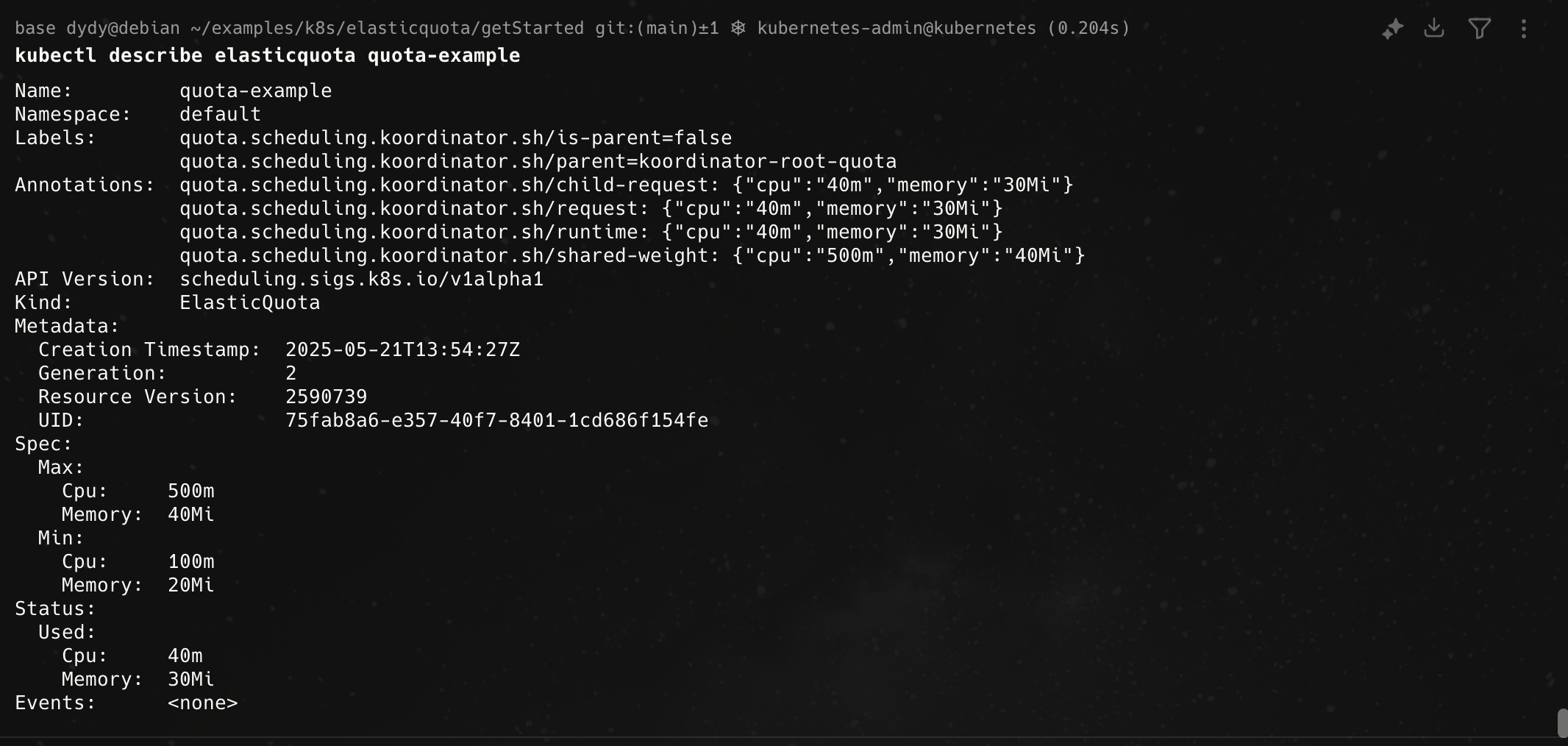
1 | |
得到当前配额资源的使用情况,得到的结果如下
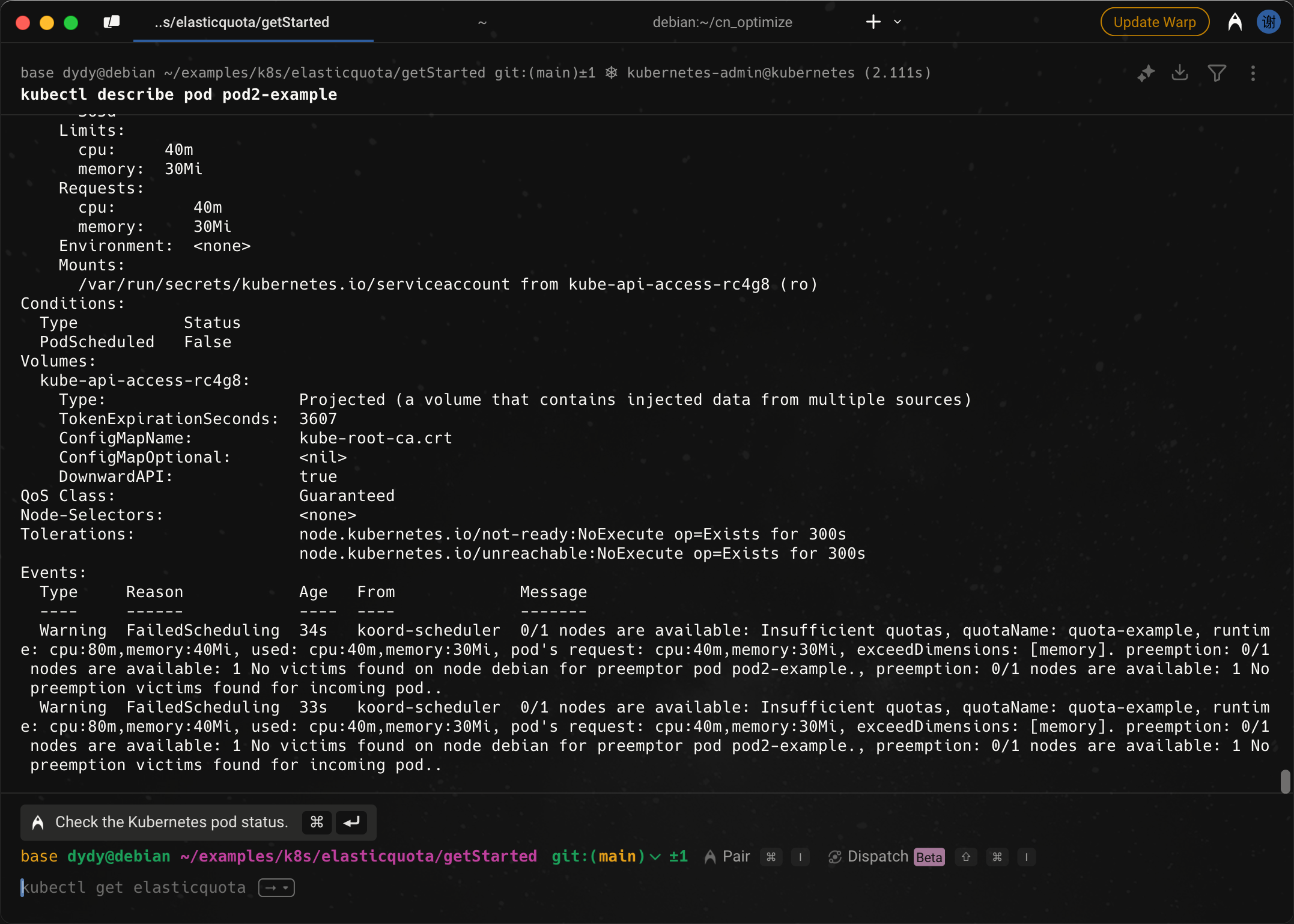
- 然后我们创建一个跟原来一样的
pods
可以看到它正在pending
把原本正在运行的pods删掉
Label 级别的抢占
前文我们已经演示了通过Label实现资源的隔离,在一个配额内我们某些高优先级的任务能够抢占低优先级的任务
- 创建优先级
class
1 | |
- 创建
elasticquota
1 | |
- 创建低优先级的
deployment
1 | |
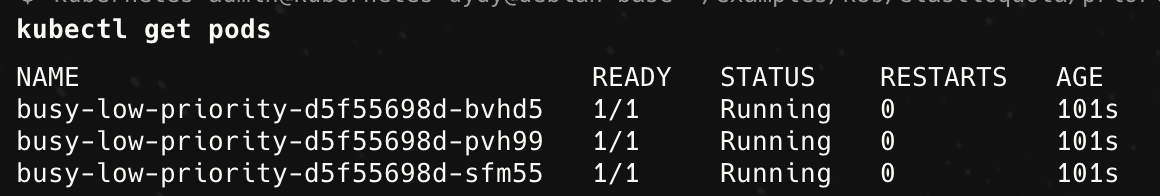
由于3个10Mi内存的pods并没有超过配额的限制,因此可以运行
- 创建高优先级的
pods
1 | |
可以看到高优先级的pods可以抢占低优先级的pods
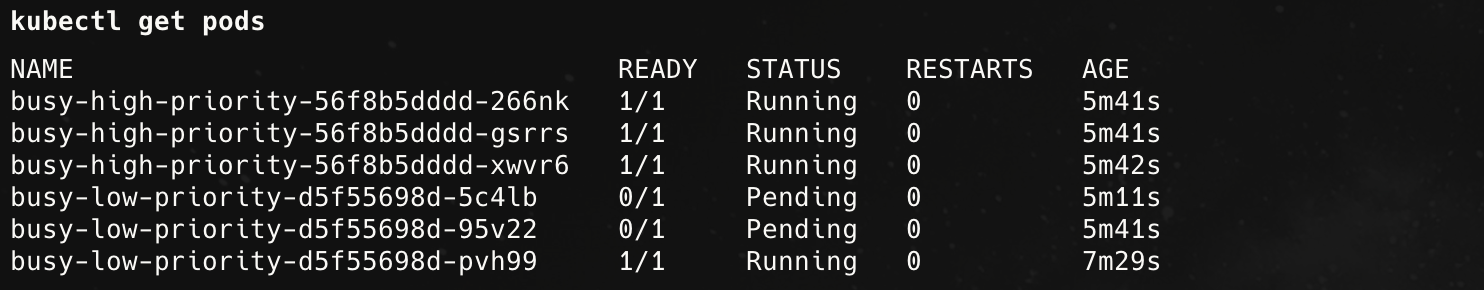
Namespaces级别的隔离
其中的namespace隔离与label隔离接口接近,这里不再赘述
代码逻辑
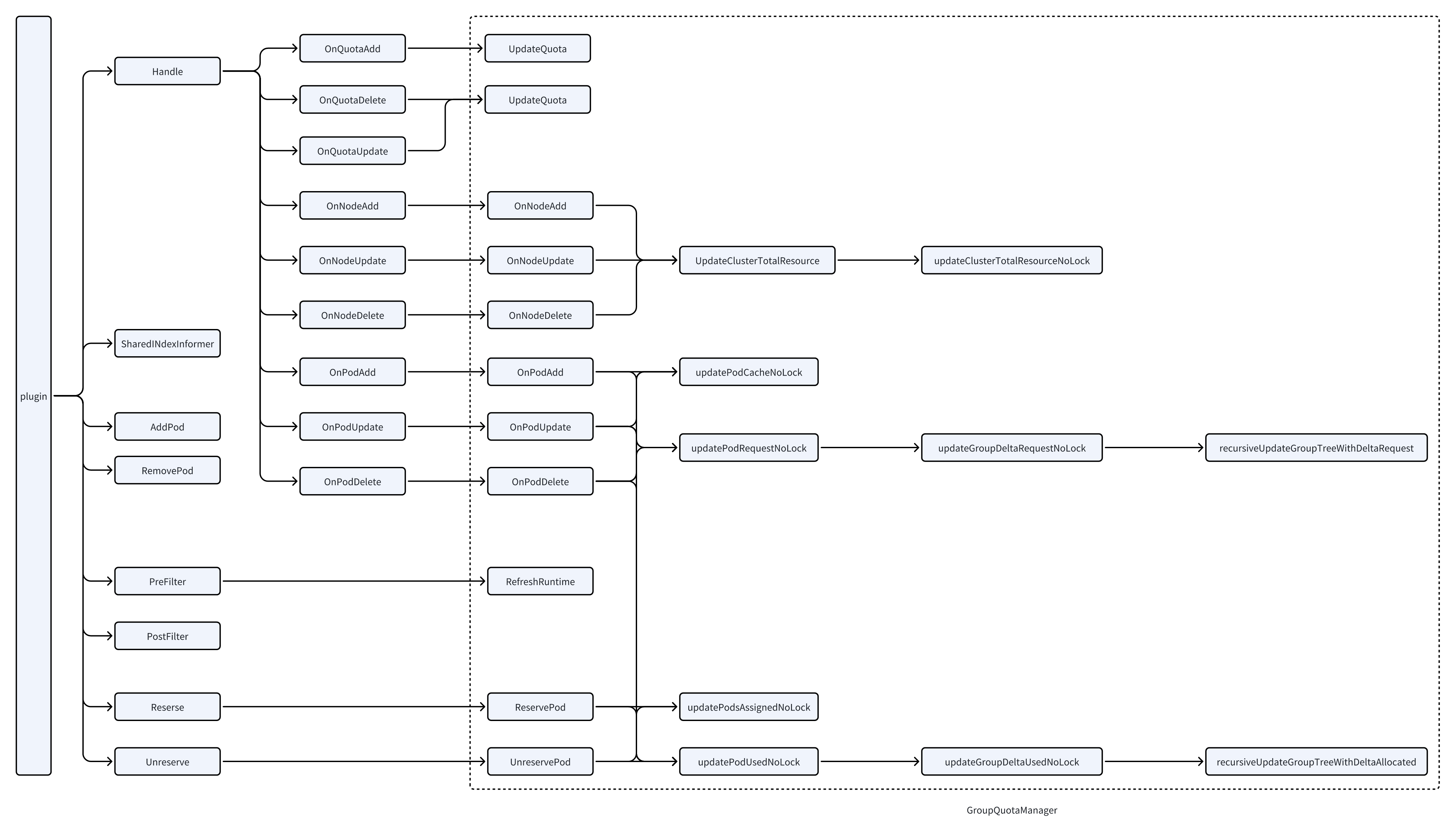
PreFilter 阶段
这个阶段主要是处理了pods加入到一个quota中,其中包含了几个重要的过程
- 检查
EnableRuntimeQuota: 这个 - 检查
pods是否是不被驱逐的pods: 将该pods加入到不被驱逐的集合当中,如果当前quota的资源不足,就拒绝这个pods - 检查
EnableCheckParentQuota: 会递归的检查当前的资源请求会不会导致父quota超额,拒绝超额的pods
PostFilter 阶段
这个阶段会修改默认的驱逐过程,只允许同个quota的pods可以互相驱逐对方
Load-aware Descheduler
代码逻辑
Balance 方法
该方法通过遍历节点池来实现重新的负载均衡,对每个节点调用processOneNodePool
- 获取节点的使用情况
getNodeUsage - 获取节点的上下限
getNodeThresholds - 将节点进行分类
classifyNodes: 分为低负载节点、高负载节点以及正常节点,分别为lowNodes, highNodes, prodLowNodes, prodHighNodes, bothLowNodes - 过滤出实际高使用量的节点
filterRealAbnormalNodes - 重置低使用量的节点
resetNodesAsNormal - 将
pods从SourceNodes中驱逐evictPodsFromSourceNodes - 尝试把高负载节点标记为正常节点
evictPodsFromSourceNodes中有一个重要的函数调用balancePods
balancePods首先将pods进行分类,分为可以删除的pods以及不可删除的- 然后将
pods排个序 - 然后驱逐
podsevictPods - 如果
continueEvictionCond条件不满足,就不会继续再驱逐pods
continueEvictionCond判定如果当前的节点压力已经没那么大了,说明就不用继续驱逐了
nodeFit
看的时候一直有一个问题,如果一个pods从高负载节点重调度到一个节点之后,导致了这个节点变为高负载该咋办?这样重调度是不是一直死循环了
nodeFit参数设置的时候在重调度过程中就会检查每个pods是否有合适的节点,如果没有设置,那么pods就会直接调度到一个节点上
podFitsAnyNodeWithThreshold 方法会检查一个pods是否有合适的节点可以接纳它
NodeFit方法会检查某个pods是否能够调度到这个节点上, 但只是一些亲和性的检查还有一些资源使用量的检查
1 | |
- 获取之后会评估这个
pod的request会不会导致node过载,如果过载就不会再调度到这个节点上